Server authentication
When configuring webhooks for your assistant, you can authenticate your server endpoints by creating Custom Credentials and referencing them using a credentialId. This approach provides better security, reusability, and centralized management of your authentication credentials.
Overview
Vapi now uses a credential-based authentication system where you:
- Create Custom Credentials through the dashboard
- Reference credentials by ID in your server configurations
- Reuse credentials across multiple assistants, phone numbers, and tools
This replaces the previous inline authentication approach and provides better security and management capabilities.
Quick start
Creating Custom Credentials
Dashboard Management
Custom Credentials are managed through the Vapi dashboard. Navigate to your organization settings to create and manage authentication credentials.
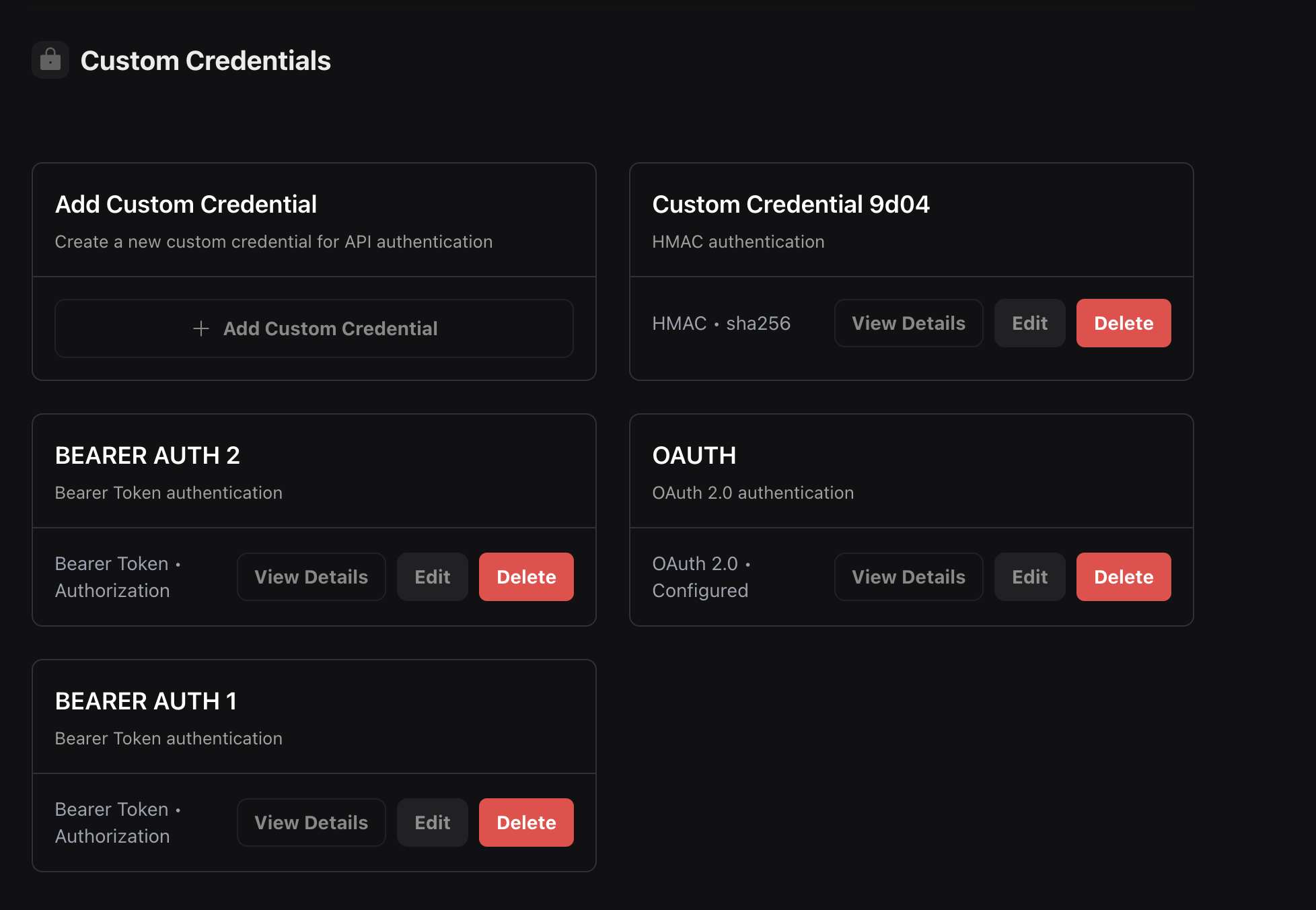
You can create different types of authentication credentials:
- Bearer Token: Simple token-based authentication
- OAuth 2.0: OAuth 2.0 client credentials flow
- HMAC: HMAC signature-based authentication
Authentication Types
Bearer Token Authentication
The most common authentication method using a bearer token in the Authorization header.
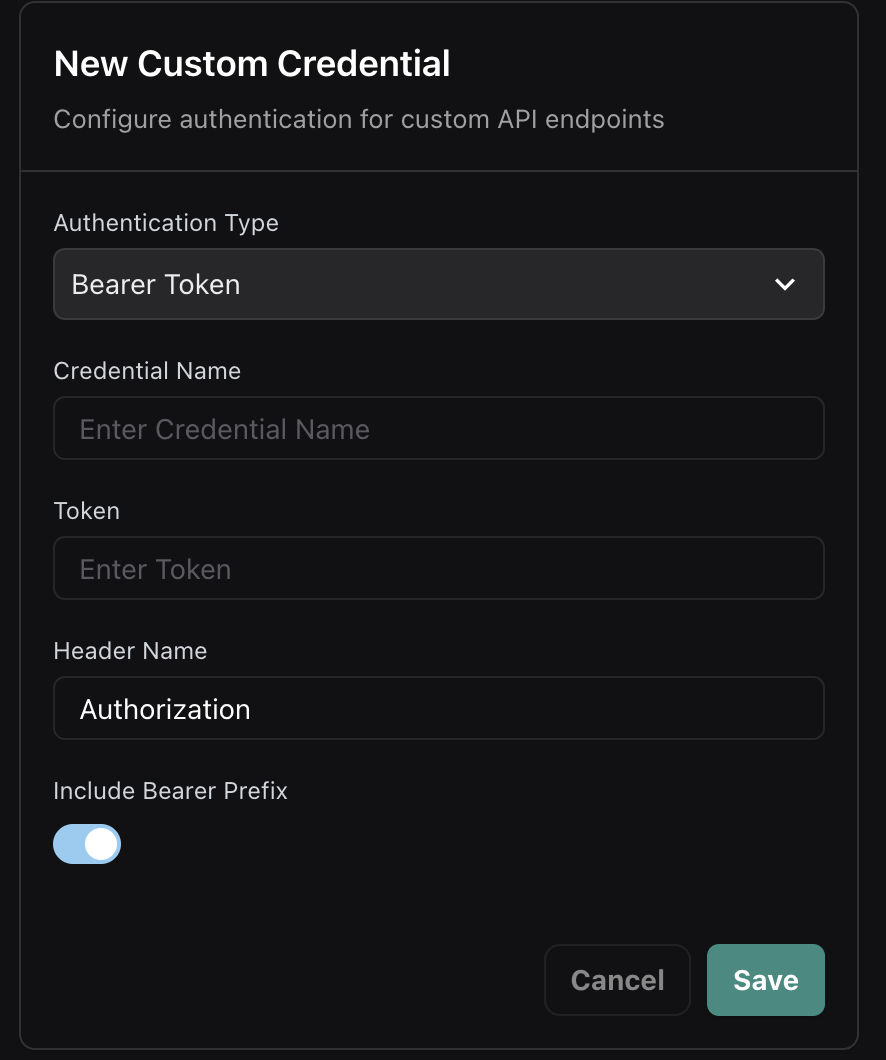
Create Bearer Token Credential
In the dashboard, select “Bearer Token” as the authentication type and configure:
- Credential Name: A descriptive name for the credential
- Token: Your API token or secret
- Header Name: The header to send the token in (default:
Authorization) - Include Bearer Prefix: Whether to prefix the token with “Bearer ”
Standard Authorization Header
The most common Bearer Token configuration uses the standard Authorization header with the Bearer prefix:
Create standard Bearer Token credential
Configure a Bearer Token credential with:
- Header Name:
Authorization(default) - Include Bearer Prefix: Enabled (toggle on)
- Token: Your API token or secret key
This is the recommended approach for modern API authentication and works with most authentication frameworks and libraries.
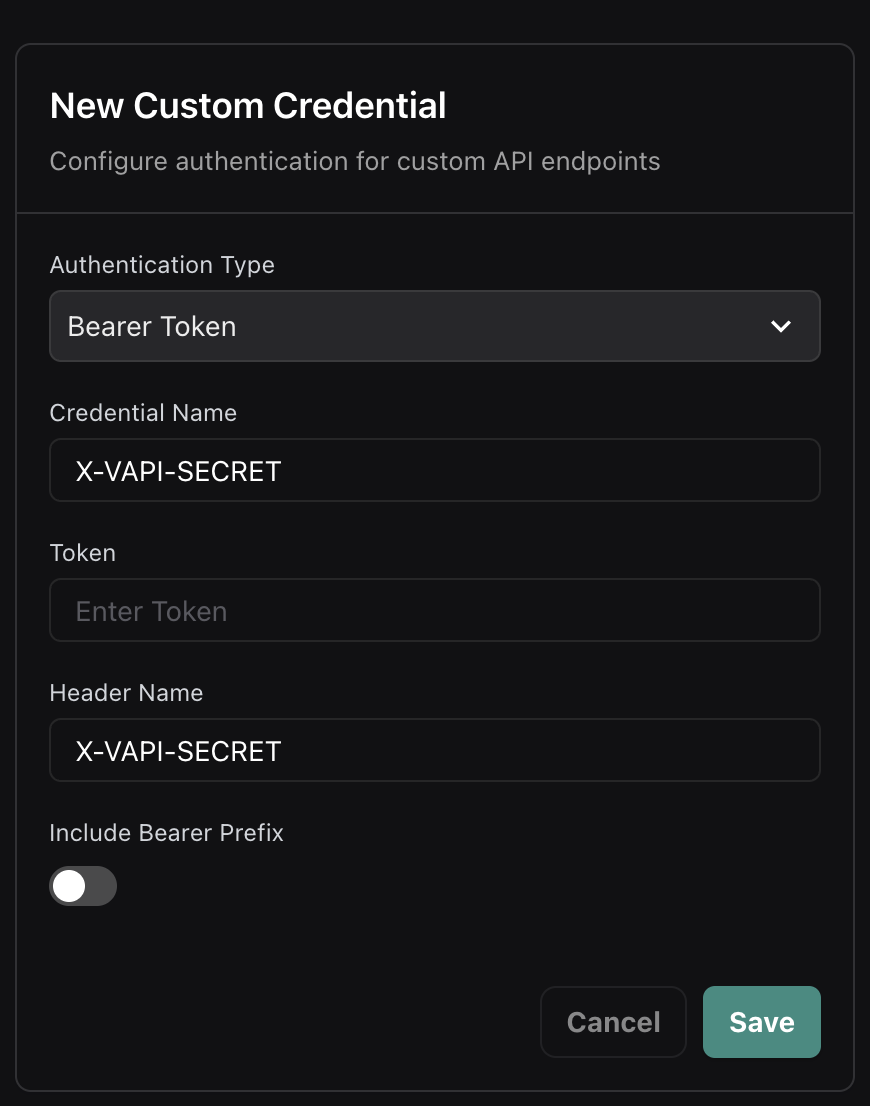
Legacy X-Vapi-Secret Support
For backward compatibility with existing implementations, you can configure a Bearer Token credential to use the X-Vapi-Secret header (matching the previous inline secret field behavior):
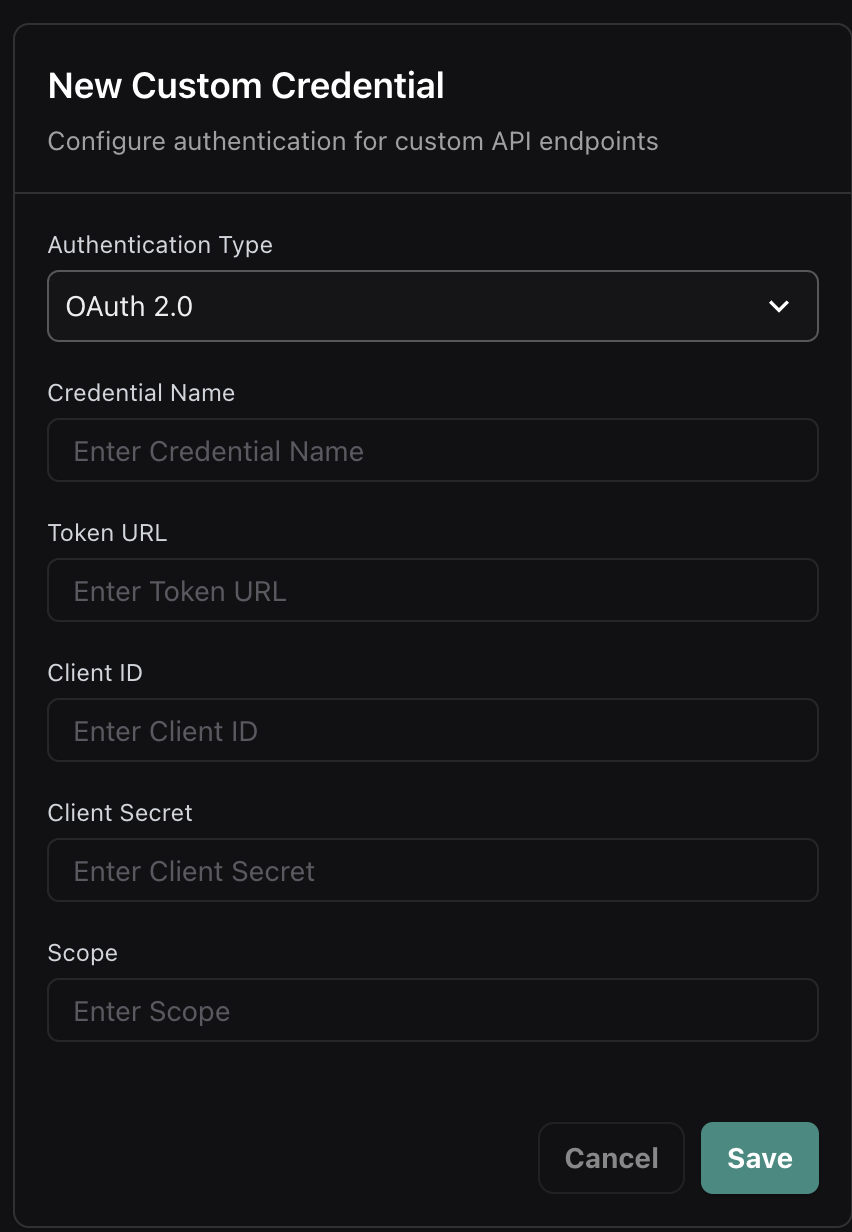
OAuth 2.0 Authentication
For OAuth 2.0 protected endpoints, configure client credentials flow with automatic token refresh.
OAuth 2.0 Flow
- Vapi makes a token request to your OAuth endpoint with client credentials
- Your server validates the credentials and returns an access token
- Vapi includes the access token in the Authorization header for webhook requests
- When tokens expire, Vapi automatically requests new ones
Token Response Format
Your OAuth server should return:
HMAC Authentication
For maximum security, use HMAC signature-based authentication to verify request integrity.
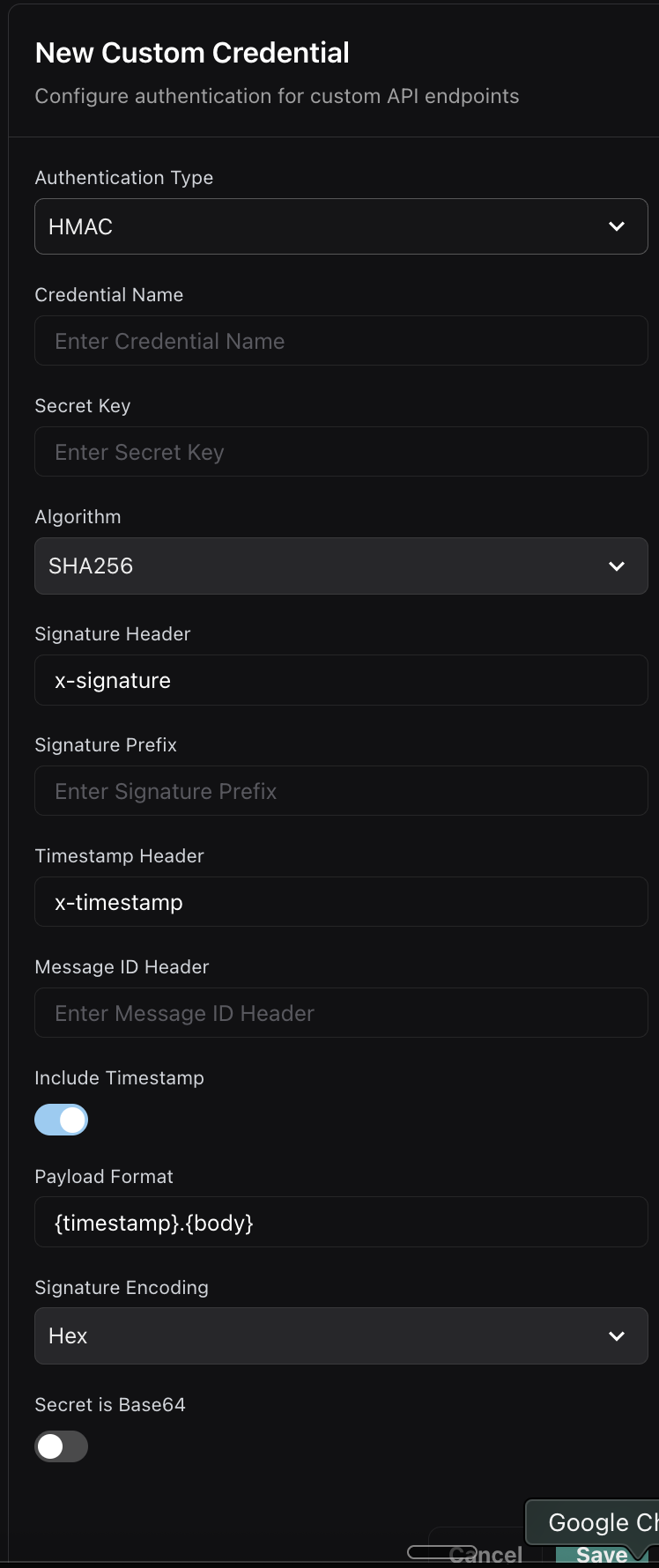
Create HMAC Credential
Select “HMAC” as the authentication type and configure:
- Credential Name: A descriptive name for the credential
- Secret Key: Your HMAC secret key
- Algorithm: Hash algorithm (SHA256, SHA1, etc.)
- Signature Header: Header name for the signature (e.g.,
x-signature) - Timestamp Header: Optional timestamp header for replay protection
- Payload Format: How to format the payload for signing
Using Credentials
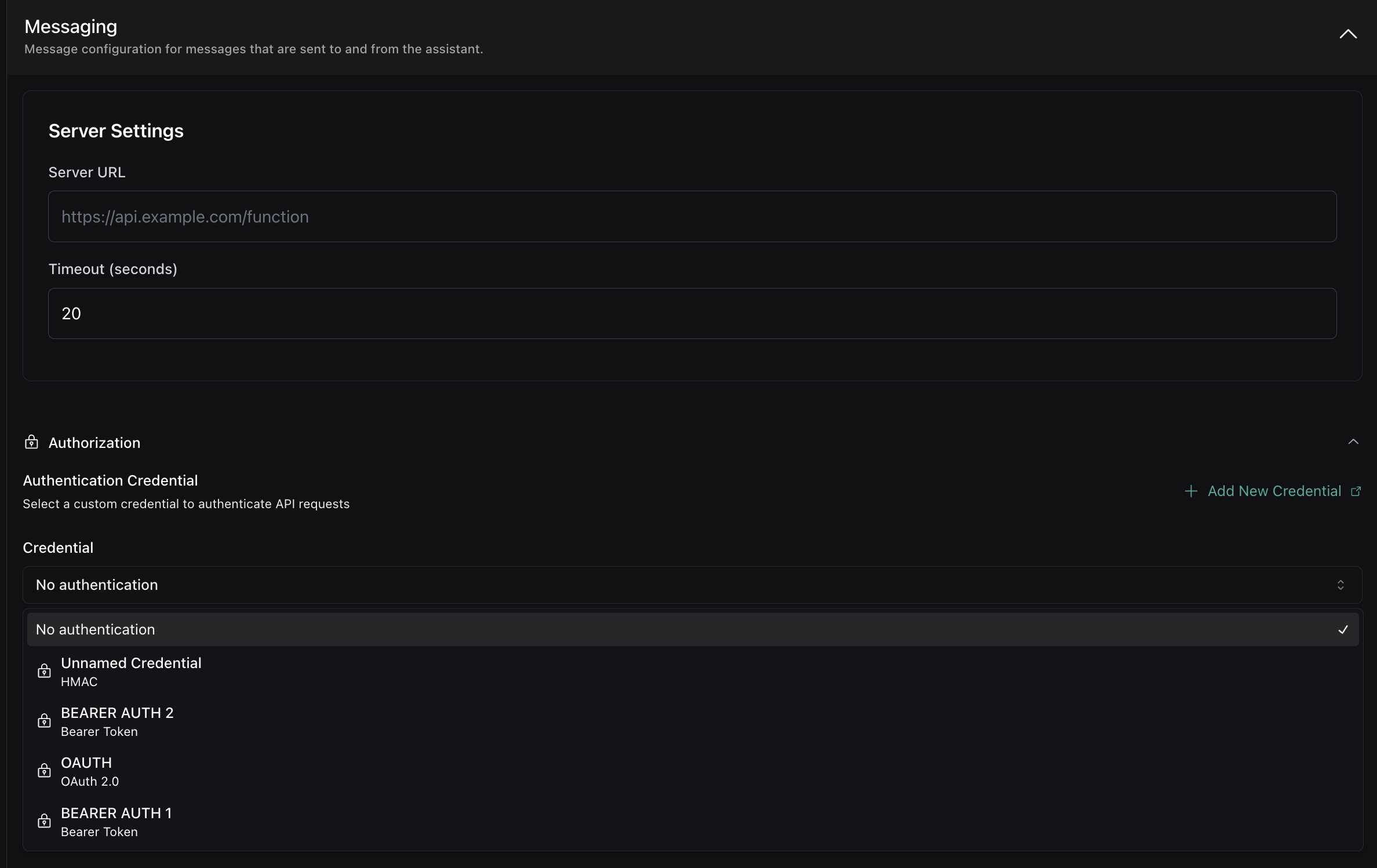
In Assistant Configuration
Reference credentials in your assistant’s server configuration:
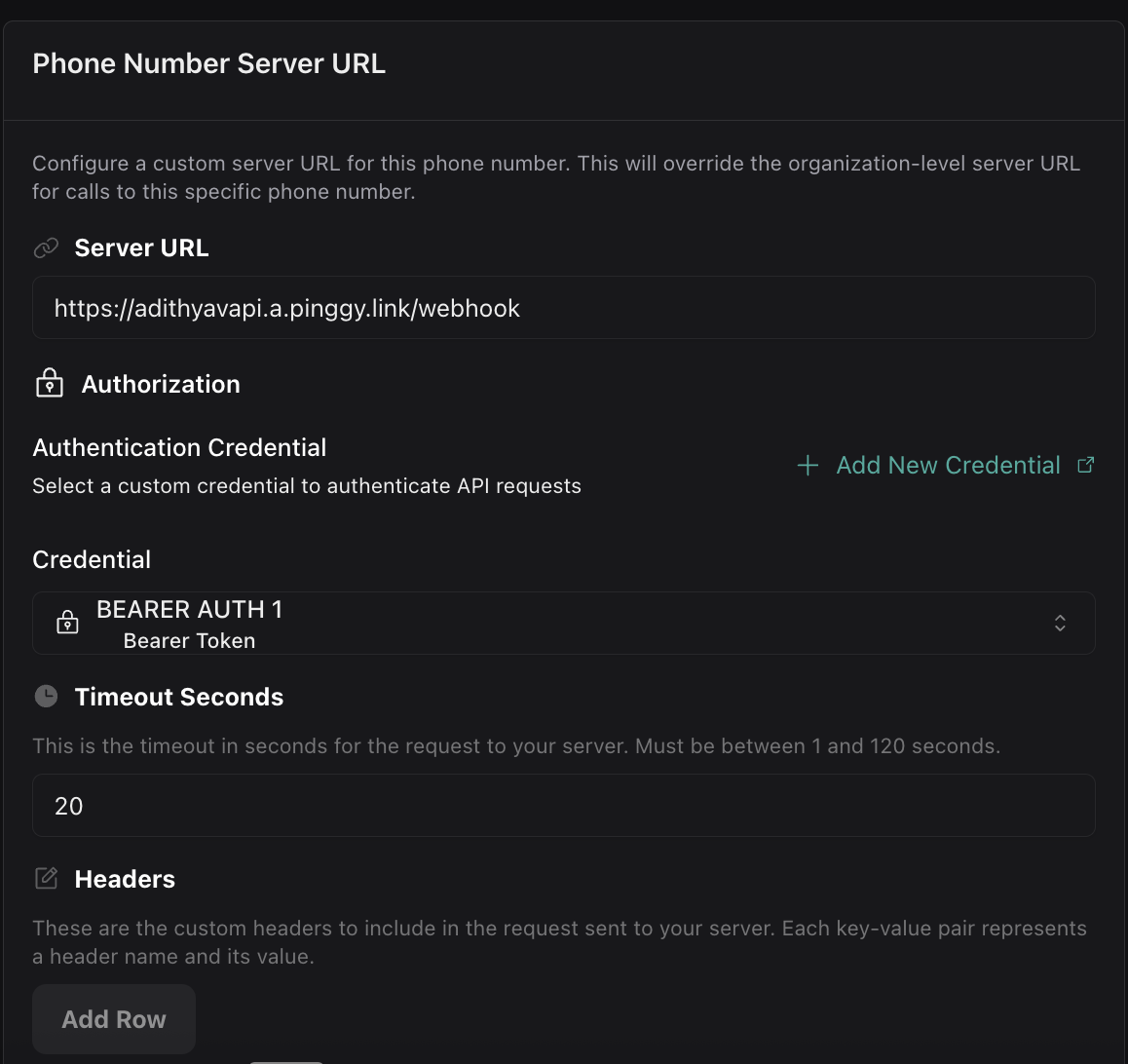
In Phone Number Configuration
Assign credentials to phone numbers for incoming call authentication:
In Tool Configuration
Secure your function tool endpoints with credentials:
Credential Management
Dashboard Features
The Custom Credentials dashboard provides:
- Credential Creation: Create new authentication credentials
- Credential Editing: Modify existing credential configurations
- Credential Deletion: Remove unused credentials
- Usage Tracking: See where credentials are being used
Best Practices
Credential Naming: Use descriptive names like “Production API Key” or “Staging OAuth” to easily identify credentials.
Credential Rotation: Regularly rotate credentials for enhanced security. Update the credential in the dashboard without changing your configurations.
Credential Security: Store credential secrets securely. Once created, secrets are encrypted and cannot be viewed in the dashboard.
Migration from Inline Authentication
If you’re currently using inline authentication, migrate to the credential system:
Create equivalent credentials
For each inline authentication configuration, create a matching Custom Credential in the dashboard:
- For
secretfield: Create a Bearer Token credential with headerX-Vapi-Secretand no Bearer prefix (see Legacy X-Vapi-Secret Support) - For
headersfield: Create a Bearer Token credential with the appropriate header name - For OAuth configurations: Create an OAuth 2.0 credential
Common Use Cases
Single Credential for Multiple Resources
Reuse the same credential across different components:
Environment-Specific Credentials
Use different credentials for staging and production:
Service-Specific Credentials
Use different credentials for different services:
Next steps
Now that you have authentication configured:
- Setting server URLs: Learn where server URLs can be configured
- Server events: Understand what webhook events Vapi sends
- Local development: Set up local webhook testing