Server URLs
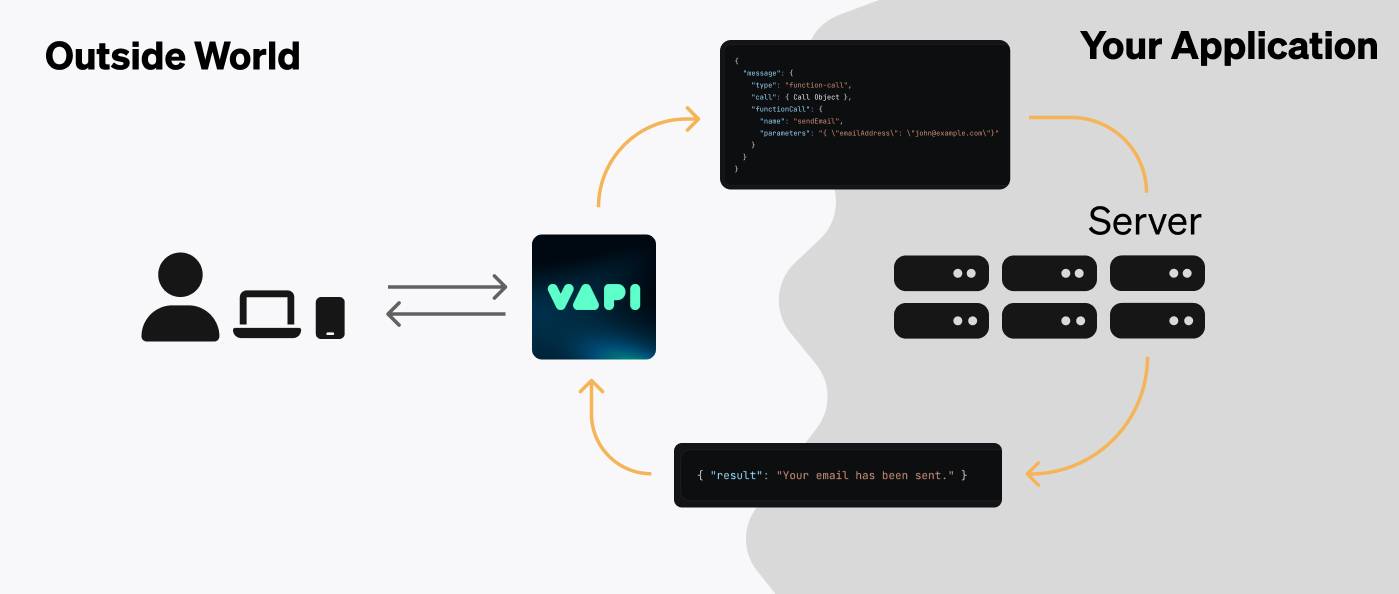
Server URLs allow your application to receive data & communicate with Vapi during conversations. Conversation events can include:
- Status Updates: updates on the status of a call
- Transcript Updates: call transcripts
- Function Calls: payloads delivered when your assistant wants certain actions executed
- Assistant Requests: in certain circumstances, Vapi may ping your server to get dynamic configuration for an assistant handling a specific call
- End of Call Report: call summary data at the end of a call
- Hang Notifications: get notified when your assistant fails to reply for a certain amount of time
In our quickstart guides we learned how to setup a basic back-and-forth conversation with a Vapi assistant.
To build more complex & custom applications, we’re going to need to get real-time conversation data to our backend. This is where server URLs come in.
If you’re familiar with functional programming, Server URLs are like callback functions. But instead of specifying a function to get data back on, we specify a URL to a server (to POST data back to).
Get Started
To get started using server URLs, read our guides:
Server URLs can be set in multiple places. Learn where here.
Read about the different types of events Vapi can send to your server.
Learn about receiving server events in your local development environment.
Forward webhooks to your local server with the Vapi CLI.
Quick local testing with Vapi CLI + tunneling:
This setup forwards webhook events to your local server. Remember to update your Vapi webhook URLs to use the ngrok public URL.
FAQ
Where can the server be located?
The server URL can be any publicly accessible URL pointing to an HTTP endpoint. This can be a:
- Cloud Server: your application might be deployed on a cloud platform like Railway, AWS, GCP, etc — as a persistent web server.
- Serverless Function: services like Vercel, AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Cloudflare, etc — allow you to host on-demand cloud functions.
- Workflow Orchestrator: platforms like Pipedream & Make allow you to program workflows (often without code) that can receive events via HTTP triggers.
The main idea is that Vapi needs a location on the Internet that it can drop data to & converse with your application.
Why not just call them webhooks?
Webhooks are traditionally unidirectional & stateless, with the target endpoint usually only replying with a status code to acknowledge message reception. Certain server URL events (like assistant requests) may require a meaningful reply from your server.
“Server URL” is a more general term that encompasses both webhooks & bidirectional communication.